Подробное руководство по использованию мультиклассовой классификации для прогнозирования футбольных результатов.
Введение
Я был вдохновлен на создание этой статьи, когда увидел, что Оксфордский университет использовал математические модели для прогнозирования исхода чемпионата мира по футболу 2022 года. Будучи заядлым футбольным фанатом и учеником в науке о данных, я решил попробовать. Футбол непредсказуем, часто не идет по пути лучшей команды, поэтому я задумался об использовании данных обо всех международных мужских матчах 2022 года. Могу ли я предсказать вероятного победителя чемпионата мира?
Данные
Я использовал два разных источника данных для этого проекта. Первыми были рейтинги, которые я скопировал с www.eloratings.net. Эти данные предоставляют рейтинги для всех мужских международных футбольных команд и используют рейтинговую систему Эло, изначально предназначенную для рейтинга шахматистов. Я также использовал данные матчей с footystats.org, чтобы собрать все мужские международные игры в 2022 году перед чемпионатом мира.
Подход
Я буду использовать многоклассовые модели классификации для решения этой проблемы, что сильно отличается от подхода, наблюдаемого в примере Оксфордского университета, в котором использовались распределения Пуассона. Я буду использовать этот подход, потому что футбол — это игра с тремя исходами — победа, поражение и ничья — и я заинтересован в применении последних знаний, полученных в университете. Модели классификации с несколькими классами можно обучать с использованием различных алгоритмов, включая деревья решений, случайные леса, методы опорных векторов и нейронные сети. Я протестирую комбинацию этих методов. Тем не менее, независимо от того, какой алгоритм используется, основная идея одна и та же: модель обучается с использованием размеченного набора данных, где каждый пример принадлежит одному из возможных классов. Модель учится делать прогнозы на основе новых данных, находя закономерности в обучающих данных, которые можно использовать для различения разных классов.
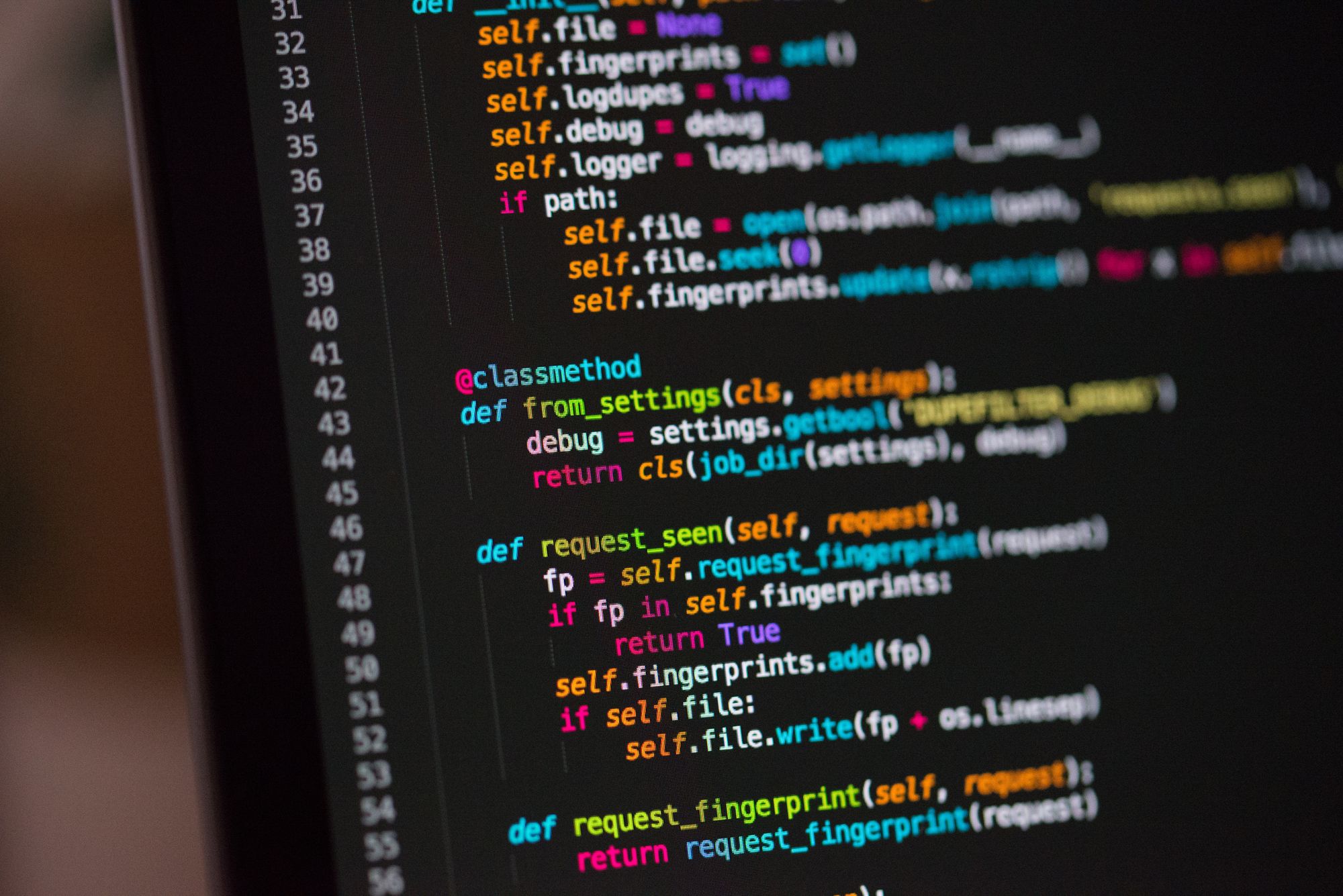
Импорт пакетов и определение функций
Чтобы начать проект, я сначала настроил блокнот Jupyter со всеми предварительными условиями, необходимыми для очистки, разработки функций/анализа и моделирования. Это включает
- Полезные пакеты
- Настройка параметров отображения для удобства использования
- Определяя функцию, мне нужно
#Importing Packages
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import poisson
import plotly.graph_objects as go
from plotly.subplots import make_subplots
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, GradientBoostingClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, train_test_split, GridSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score,f1_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report, multilabel_confusion_matrix
import itertools
import networkx as nx
from networkx.drawing.nx_pydot import graphviz_layout
#Setting Display parameters
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 1000)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 500)
pd.set_option('display.width', 1200)
pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', 200)
#Defining Functions
#A function to display Confusion Matrix and Classification Reports for Multiclass Classification Algorithms
def Multiclass_Analysis(X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test, model, labels):
y_predict_test = model.predict(X_test)
print("\n")
print('TESTING RESULTS')
print("\n")
print(classification_report(y_test, y_predict_test, target_names=labels, digits=3))
test_cm = multilabel_confusion_matrix(y_test, y_predict_test)
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(ncols=3,sharey=True, figsize = (7,3))
heatmaps(test_cm, ax1, 0, 'Win')
heatmaps(test_cm, ax2, 1, 'Loss')
heatmaps(test_cm, ax3, 2, 'Draw')
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
plt.clf()
y_predict_train = model.predict(X_train)
print("\n")
print('TRAINING RESULTS')
print("\n")
print(classification_report(y_train, y_predict_train, target_names=labels, digits=3))
train_cm = multilabel_confusion_matrix(y_train, y_predict_train)
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(ncols=3,sharey=True, figsize = (7,3))
heatmaps(train_cm, ax1, 0, 'Win')
heatmaps(train_cm, ax2, 1, 'Loss')
heatmaps(train_cm, ax3, 2, 'Draw')
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
#A function to plot Confusion Matrix for Multiclass Classification Algorithms
def heatmaps(cm_list, axis, index, label):
cm = cm_list[index]
cm[0][0] = 0
sns.heatmap(cm, cmap= 'GnBu', annot=True, fmt='g', annot_kws={'size':15}, ax=axis)
axis.set_xlabel('Predicted', fontsize=12)
axis.set_ylabel('Actual', fontsize=12)
axis.set_title(label, fontsize=12)
#A function to return result and points awarded for a football game
def result_finder(home, away):
if home > away:
return pd.Series([0, 3, 0])
if home < away:
return pd.Series([1, 0, 3])
else:
return pd.Series([2, 1, 1])
#A function to position distributions
def find_column_row_number(number_of_values):
col_num = number_of_values
rows = np.floor(np.sqrt(col_num))
while(col_num % rows != 0):
rows = rows - 1
if col_num/rows > 3:
cols = 3
rows = int(np.ceil(col_num/cols))
else:
cols = int(rows)
rows = int(col_num/rows)
if cols > rows:
cols, rows = rows, cols
return cols, rows
#A function to plot distributions
def plot_distribution(df, columns, plot):
col_num = len(columns)
cols, rows = find_column_row_number(col_num)
combinations = list(itertools.product(range(1, rows+1), range(1, cols+1)))[:col_num]
combinations_dict = {columns[i]: combinations[i] for i in range(col_num)}
fig = make_subplots(rows=rows, cols=cols, subplot_titles=(columns))
if plot == 'H':
for c, fig_info in combinations_dict.items():
row_num, col_num = fig_info
fig.add_trace(go.Histogram(x=df[c], name = c, opacity=0.7), row= row_num, col= col_num)
if plot == 'B':
for c, fig_info in combinations_dict.items():
row_num, col_num = fig_info
fig.add_trace(go.Box(x=df[c], name = c, opacity=0.7), row= row_num, col= col_num)
fig.update_yaxes(showticklabels=False)
if plot == 'V':
for c, fig_info in combinations_dict.items():
row_num, col_num = fig_info
fig.add_trace(go.Violin(x=df[c], name = c, box_visible=True, meanline_visible=True, opacity=0.7), row= row_num, col= col_num)
fig.update_yaxes(showticklabels=False)
fig.update_layout(showlegend = False,
autosize=False,
width=1000,
height=1200,
template = 'plotly_white')
fig.show()
#A function to find the best set of parameters
def BestParameters(X, y, model_params):
scores = []
for model_name, mp in model_params.items():
clf = GridSearchCV(mp['model'], mp['params'], cv=3, scoring = 'f1_weighted', return_train_score=True, verbose=2)
clf.fit(X, y)
results = pd.DataFrame(clf.cv_results_)
results = results.sort_values(by='rank_test_score').reset_index(drop=True)
return results
Очистка данных
Затем я перешел к этапу очистки моего проекта, который повлек за собой:
- Импорт данных
- Преобразование данных, чтобы их можно было фильтровать
- Фильтрация данных для правильного периода времени
- Объединение наборов данных
- Создание нескольких ценных функций
- & Расширение фрейма данных, чтобы позволить каждой команде иметь уникальные строки для каждой игры, в которой они принимали участие.
Я расширил фреймворк данных, чтобы убедиться, что могу создавать функции домашней и выездной команды.
#Importing Data
rating = pd.read_csv('international_elo_rating.csv')
fixtures = pd.read_csv('international_recent_fixtures.csv')
#Created Day and Time Columns from "date_GMT"
fixtures[['day','time']] = fixtures['date_GMT'].str.split(" - ",expand=True)
#Made Datetime Column from newly created "day"
fixtures['date'] = pd.to_datetime(fixtures['day'], format='%b %d %Y')
#Filtered data for matches that have taken place in 2022
fixtures = fixtures.loc[(fixtures.status == 'complete')]
fixtures = fixtures.loc[(fixtures.date.dt.to_period('Y') == '2022')].reset_index(drop=True)
#Selected Useful Columns
fixtures = fixtures[['date', 'home_team_name','away_team_name','home_team_goal_count', 'away_team_goal_count', 'team_a_xg', 'team_b_xg', 'home_team_possession', 'away_team_possession']]
#Found elo ratings for Home and Away Teams
team_rating = rating[['team', 'current_rating']]
opposition_rating = rating[['team', 'current_rating']]
team_rating.columns = ['home_team_name', 'home_team_rating']
opposition_rating.columns = ['away_team_name', 'away_team_rating']
#Joined Team Ratings with Fixtures
fixtures = pd.merge(fixtures, team_rating, on='home_team_name', how = 'left')
fixtures = pd.merge(fixtures, opposition_rating, on='away_team_name', how = 'left')
#Dropped Duplicates
fixtures= fixtures.drop_duplicates()
#Used Pre-defined Function to create my target column - Results and assign points to teams
results = fixtures.apply(lambda x: result_finder(x["home_team_goal_count"], x["away_team_goal_count"]), axis=1)
fixtures[["result", "home_team_points", "away_team_points"]] = results
#Expanded Dataframe so each fixture was broken up into 2 rows on for the away to and one for the home
home_team = fixtures[['date','home_team_name','home_team_goal_count', 'away_team_goal_count', 'team_a_xg', 'team_b_xg', 'home_team_possession', 'away_team_possession', 'home_team_rating', 'away_team_rating', 'result', 'home_team_points']]
away_team = fixtures[['date','away_team_name','home_team_goal_count', 'away_team_goal_count', 'team_a_xg', 'team_b_xg', 'away_team_possession', 'home_team_possession', 'away_team_rating', 'home_team_rating', 'result', 'away_team_points']]
home_team.columns = ['date','team_name', 'goals_scored', 'goals_conceeded', 'xg', 'xga', 'possession', 'opponents_possession', 'rating', 'opponents_rating', 'result', 'team_points']
away_team.columns = ['date','team_name', 'goals_conceeded', 'goals_scored', 'xga', 'xg', 'possession', 'opponents_possession', 'rating', 'opponents_rating', 'result', 'team_points']
home_team = home_team[['date','team_name', 'goals_scored', 'goals_conceeded', 'xg', 'xga', 'possession', 'opponents_possession', 'rating', 'opponents_rating', 'result', 'team_points']]
away_team = away_team[['date','team_name', 'goals_scored', 'goals_conceeded', 'xg', 'xga', 'possession', 'opponents_possession', 'rating', 'opponents_rating', 'result', 'team_points']]
team_info= pd.concat([home_team, away_team]).sort_values("date").reset_index(drop=True)
Разработка функций
Затем я перешел к элементу Feature Engineering моего проекта, где я сделал большую часть своих функций. Это включает:
- Среднее ожидаемое количество голов — avg_xg — количество голов, которое команда ожидает забить в среднем в зависимости от качества использованных моментов.
- Среднее ожидаемое количество голов против — avg_xga — количество голов, которое команда ожидает пропустить в среднем, исходя из качества имеющихся моментов.
- Average Possession For — avg_poss_for — среднее количество владения мячом командой.
- Average Possession For — avg_poss_agn — среднее количество владения мячом командой соперника.
- Average Goals For — avg_goals_for — среднее количество голов, забитых командой.
- Average Goals Against — avg_goals_agn — среднее количество голов, которое команда пропускает.
- Средний рейтинг — avg_rating — средний рейтинг Эло команды.
- Средний рейтинг оппонентов — avg_opponents_rating — средний рейтинг Эло оппонентов, с которыми они столкнулись.
- Средние баллы — avg_points — средний балл, начисленный команде.
Затем я сделал функции, производные от первоначальных функций, которые показали различия этих функций.
Я завершил этап разработки признаков, отбросив недостающие значения и создав окончательный фрейм данных, который будет использоваться после этапа анализа признаков для создания модели.
#Feature Creation
#Creating Aggregate Features for Each Team
agg_features = team_info.groupby('team_name', as_index=False).agg(avg_xg=pd.NamedAgg(column="xg", aggfunc="mean"),
avg_xga=pd.NamedAgg(column="xga", aggfunc="mean"),
avg_poss_for=pd.NamedAgg(column="possession", aggfunc="mean"),
avg_poss_agn=pd.NamedAgg(column="opponents_possession", aggfunc="mean"),
avg_goals_for=pd.NamedAgg(column="goals_scored", aggfunc="mean"),
avg_goals_agn=pd.NamedAgg(column="goals_conceeded", aggfunc="mean"),
avg_rating=pd.NamedAgg(column="rating", aggfunc="mean"),
avg_opponents_rating=pd.NamedAgg(column="opponents_rating", aggfunc="mean"),
avg_points=pd.NamedAgg(column="team_points", aggfunc="mean"))
#Creating Avg Differences between teams and their opposition
agg_features['avg_dif_xg'] = agg_features['avg_xg'] - agg_features['avg_xga']
agg_features['avg_dif_poss'] = agg_features['avg_poss_for'] - agg_features['avg_poss_agn']
agg_features['avg_dif_goals'] = agg_features['avg_goals_for'] - agg_features['avg_goals_agn']
agg_features['avg_dif_rating'] = agg_features['avg_rating'] - agg_features['avg_opponents_rating']
#Creating all features Home and Away
home_agg_features = agg_features.copy()
away_agg_features = agg_features.copy()
home_agg_features.columns = ['home_'+str(col) for col in home_agg_features.columns]
away_agg_features.columns = ['away_'+str(col) for col in away_agg_features.columns]
#Merging Features with Games
df = fixtures[['date','home_team_name','away_team_name', 'result']]
df = pd.merge(df, home_agg_features, on='home_team_name', how = 'inner')
df = pd.merge(df, away_agg_features, on='away_team_name', how = 'inner')
#Creating Dataframe with inversed fixtures to remove any home or away bias
df_inversed = fixtures[['date','away_team_name', 'home_team_name', 'result']]
df_inversed.columns = ['date','home_team_name','away_team_name', 'result']
df_inversed = df_inversed.replace(0, 3)
df_inversed = df_inversed.replace(1, 4)
df_inversed = df_inversed.replace(4, 0)
df_inversed = df_inversed.replace(3, 1)
df_inversed = pd.merge(df_inversed, home_agg_features, on='home_team_name', how = 'inner')
df_inversed = pd.merge(df_inversed, away_agg_features, on='away_team_name', how = 'inner')
#Creating Final Dataframe
final_df = pd.concat([df, df_inversed]).sort_values("date").reset_index(drop=True)
#Removing matches where XG and XGA is not recorded
final_df = final_df.loc[(final_df.home_avg_xg != 0) & (final_df.away_avg_xg != 0)]
#Finding Missing Values
missing_count = final_df.isnull().sum()
missing_df = pd.DataFrame({'column':missing_count.index, 'missing_count':missing_count.values})
missing_df = missing_df.sort_values(by= ['missing_count'], ascending=False).reset_index(drop=True)
display(missing_df)
#Dropping Missing Values
final_df = final_df.dropna()
Анализ и выбор функций
Чтобы начать анализ признаков, я искал мультиколлинеарность и отбрасывал коллинеарные признаки, используя тепловую карту.
#Making Features Dataframe
features = final_df.iloc[:, 4:]
#Setting size for Correlation Matrix
plt.figure(figsize=(12,12))
#Creating Correlation Data
corr_matrix = features.corr()
#Plotting Correlation Matrix
sns.heatmap(
corr_matrix,
annot=True,
annot_kws={"fontsize": 10},
linewidths=0.5,
center=0.00,
fmt=".2f",
xticklabels=corr_matrix.columns,
yticklabels=corr_matrix.columns,
cmap = sns.diverging_palette(10, 240, n=9),
vmin=-1,
vmax=1)
plt.show()
Затем я посмотрел на распределения функций, которые я создал. Я гарантировал, что все они были относительно нормально распределены, так как это одно из предположений для большинства моделей машинного обучения.
Dropping Collinear Features features = features.drop(['home_avg_poss_for','home_avg_poss_agn', 'home_avg_dif_goals', 'away_avg_dif_goals', 'away_avg_points', 'away_avg_poss_for'], axis=1) #Plotting Distributions of Features plot_distribution(features,features.columns, 'H')
Моделирование, настройка гиперпараметров и оценка
Затем я создал сетку параметров, которую использовал для хранения переменных гиперпараметров и подходов к классификации, которые хотел протестировать. Затем я использовал это в качестве входных данных для GridSearchCV, который использует перекрестную проверку и итерацию по заданной сетке параметров, чтобы найти лучшие гиперпараметры на основе метрики оценки. В этом примере я использовал взвешенную оценку F1. Предопределенная функция «BestParameters» использовалась для вывода лучших результатов. Затем я нашел набор параметров, которые возвращали высокие баллы как за поезд, так и за тест, и использовал эти параметры для моей окончательной модели.
#Creating the models and hypertuning parameters
model_params = {
'decision_tree': {
'model': DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42),
'params': {
'criterion': ['gini','entropy'],
'min_samples_split' : list(range(2,10)),
'min_samples_leaf' : list(range(2,10)),}},
'random_forrest': {
'model': RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42),
'params': {
"n_estimators" : [100, 300, 500, 800, 1200],
"max_depth" : [5, 8, 15, 25, 30],
"min_samples_split" : [2, 5, 10, 15, 100],
"min_samples_leaf" : [1, 2, 5, 10] ,
"max_features": ["sqrt"]}},
'gradient_boosting': {
'model': GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=42),
'params': {
"learning_rate": [0.01, 0.1, 0.5],
"min_samples_split": [5, 10],
"min_samples_leaf": [3, 5],
"max_depth":[3,5,10],
"max_features":["sqrt"],
"n_estimators":[100, 200]}}
#Making Features and Labels
X = features
y = final_df.result
#Using Param Grid defined to find the best model
clf_df = BestParameters(X, y, model_params)
#Displaying the top 10 best models
display(clf_df.head(10)[['rank_test_score', 'params', 'mean_test_score', 'mean_train_score']])
#Creating Train and Test Data X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size= 0.2, random_state=1) #Fitting Model with Best Parameters gb = GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=42, learning_rate = 0.01, max_depth = 3, max_features = 'sqrt', min_samples_leaf = 3, min_samples_split = 10, n_estimators = 200) gb.fit(X_train.values, np.ravel(y_train)) #Creating Confusion Matrix labels = ['Win','Loss','Draw'] Multiclass_Analysis(X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test, gb, labels) #Retraining Model with all the Data gb = GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=42, learning_rate = 0.01, max_depth = 3, max_features = 'sqrt', min_samples_leaf = 3, min_samples_split = 10, n_estimators = 200) gb.fit(X.values, np.ravel(y)
Затем я проанализировал показатели прогнозирования выбранной мной модели с помощью отчета о классификации и матрицы путаницы, созданной моей предопределенной функцией. Поскольку я предсказываю мультиклассовую классификацию, я удалил предсказание истинных отрицательных результатов для ясности визуализации.
Прогнозирование результатов игры
Поскольку я нашел модель, которую буду использовать, я мог начать самое интересное. Время предсказывать чемпионат мира! В ходе многих итераций своих блокнотов я создал показанную ниже функцию, которая прогнозирует и выводит результаты в зависимости от играющих команд и стадии соревнования.
def knockout_stage_simulator(fixtures, stage=None, tracking_list=None):
for i, fixture in enumerate(sorted(fixtures)):
game = fixture[0]
team_1 = fixture[1]
team_2 = fixture[2]
team_1_home_features = world_cup[team_1]['HomeFeatures']
team_1_away_features = world_cup[team_1]['AwayFeatures']
team_2_home_features = world_cup[team_2]['HomeFeatures']
team_2_away_features = world_cup[team_2]['AwayFeatures']
normal = [team_1_home_features + team_2_away_features]
inversed = [team_2_home_features + team_1_away_features]
prob_1 = gb.predict_proba(normal)
prob_2 = gb.predict_proba(inversed)
win_percentage = (prob_1[0][0] + prob_2[0][1])/2
loss_percentage = (prob_1[0][1] + prob_2[0][0])/2
draw_percentage = (prob_1[0][2] + prob_2[0][2])/2
prob_list = [win_percentage, loss_percentage, draw_percentage]
result = prob_list.index(max(prob_list))
if stage == 'GS':
world_cup[team_1]['AverageWinPercentage'] += win_percentage/3
world_cup[team_2]['AverageWinPercentage'] += loss_percentage/3
if result == 0:
print(f"Group {game} - {team_1} vs {team_2} : {team_1} Win with a Probability of {round(win_percentage,2)}")
world_cup[team_1]['GroupPoints'] +=3
elif result == 1:
print(f"Group {game} - {team_1} vs {team_2} : {team_2} Win with a Probability of {round(loss_percentage,2)}")
world_cup[team_2]['GroupPoints'] +=3
else:
print(f"Group {game} - {team_1} vs {team_2} : The Game Results in a Draw with a Probability of {round(draw_percentage,2)}")
world_cup[team_1]['GroupPoints'] +=1
world_cup[team_2]['GroupPoints'] +=1
if (i+1) % 6 == 0:
sorted_groups = sorted({team : [world_cup[team]["GroupPoints"], world_cup[team]["AverageWinPercentage"]] for team in world_cup_group_stages[game]}.items(), key=lambda p:p[1], reverse=True)
winner = sorted_groups[0][0]
second = sorted_groups[1][0]
group_winners_list.append(winner)
group_second_list.append(second)
print("\n")
print(f"Group {group} Standings :")
for k,v in sorted_groups:
print(f"{k} -- {v[0]}")
print("\n")
if stage in ['R16', 'Q', 'S']:
result_list = [team_1, team_2, round(win_percentage, 2), round(loss_percentage,2)]
knockout_games.append(result_list)
if result == 2:
min_prob = prob_list.index(min(prob_list))
if min_prob == 0:
result = 1
else:
result = 0
if result == 0:
print(f"Game {game} - {team_1} vs {team_2} : {team_1} Win with a Probability of {round(win_percentage,2)}")
tracking_list.append(team_1)
if stage == 'S':
tracking_list[0].append(team_1)
tracking_list[1].append(team_2)
else:
print(f"Game {game} - {team_1} vs {team_2} : {team_2} Win with a Probability of {round(loss_percentage,2)}")
tracking_list.append(team_2)
if stage == 'S':
tracking_list[0].append(team_2)
tracking_list[1].append(team_1)
if stage == 'F':
if game == 1:
result_list = [team_1, team_2, round(win_percentage, 2), round(loss_percentage,2)]
knockout_games.append(result_list)
if result == 0:
print(f"World Cup Final - {team_1} vs {team_2} : {team_1} Win the World Cup Final! with a Probability of {round(win_percentage,2)}")
else:
print(f"World Cup Final - {team_1} vs {team_2} : {team_2} Win the World Cup Final! with a Probability of {round(loss_percentage,2)}")
else:
if result == 0:
print(f"World Cup Third Place - {team_1} vs {team_2} : {team_1} Win the World Cup Third Place! with a Probability of {round(win_percentage,2)}")
else:
print(f"World Cup Third Place - {team_1} vs {team_2} : {team_2} Win the World Cup Third Place! with a Probability of {round(loss_percentage,2)}")
Создание хранилища данных
Я создал различные структуры данных, включая списки и вложенные словари, для хранения команд, групп, фикстур и прогнозов, выводимых моделью.
#A list of teams in the world cup
world_cup_teams = ["Qatar", "Ecuador", "Senegal", "Netherlands", "England", "Iran", "United States", "Wales", "Argentina", "Saudi Arabia", "Mexico", "Poland", "France", "Australia", "Denmark", "Tunisia", "Spain", "Costa Rica", "Germany", "Japan", "Belgium", "Canada", "Morocco", "Croatia", "Brazil", "Serbia", "Switzerland", "Cameroon", "Portugal", "Ghana", "Uruguay", "South Korea"]
#A list of the teams corresponding groups
world_cup_groups = ["A", "A", "A", "A","B", "B", "B", "B","C", "C", "C", "C", "D", "D", "D", "D", "E", "E", "E", "E", "F", "F", "F", "F", "G", "G", "G", "G", "H", "H", "H", "H"]
#Creating a dictionary to hold team data
world_cup = {team: {"Group" : group, "GroupPoints" : 0, "AverageWinPercentage": 0, "HomeFeatures" : list(home_features.loc[(home_features.home_team_name == team)].values[0][1:]), "AwayFeatures" : list(away_features.loc[(away_features.away_team_name == team)].values[0][1:])} for team, group in zip(world_cup_teams, world_cup_groups)}
world_cup_group_stages = {"A":[], "B":[], "C":[], "D":[], "E":[], "F":[], "G":[], "H":[]}
world_cup_group_fixtures = []
#Creating a dictionary to hold data about which group each team is assigned to
for team, group in zip(world_cup_teams, world_cup_groups):
world_cup_group_stages[group].append(team)
#Creating a the fixtures for the group stages
for k in world_cup_group_stages.keys():
print()
group_k_games = list(itertools.combinations(world_cup_group_stages[k], 2))
for j in range(len(group_k_games)):
world_cup_group_fixtures.append([k] + list(group_k_games[j]))
#Creating list to store results data
group_winners_list = []
group_second_list = []
round_16_winners_list = []
quater_final_winners_list = []
semi_final_winners_list = []
semi_final_second_list = []
knockout_games = []
#Creating list to store fixture data
world_cup_round_16_fixtures = []
world_cup_quater_final_fixtures = []
world_cup_semi_final_fixtures = []
world_cup_final_fixtures = []
Моделирование матчей
Затем я использовал функцию прогнозирования в тандеме с циклами for, создающими приспособления, для моделирования чемпионата мира от группового этапа до финала. Результат этого показан в нижней части учебника.
#Simulating Group Stages
print("Group Stages \n")
knockout_stage_simulator(world_cup_group_fixtures, stage='GS', tracking_list=[group_winners_list, group_second_list])
#Creating Fixtures for Round of 16
for i in range(8):
if i % 2 == 0:
world_cup_round_16_fixtures.append([int((i/2) +1), group_winners_list[i], group_second_list[i+1]])
else:
world_cup_round_16_fixtures.append([int(((i-1)/2) + 5), group_winners_list[i], group_second_list[i-1]])
#Simulating Round of 16
print("\n Round of 16 \n")
knockout_stage_simulator(world_cup_round_16_fixtures, stage='R16', tracking_list=round_16_winners_list)
#Creating Fixtures for Quarter Finals
for i in range(0, 8, 2):
world_cup_quater_final_fixtures.append([int((i/2)+1),round_16_winners_list[i], round_16_winners_list[i+1]])
#Simulating Quarter Finals
print("\n Quarter Finals \n")
knockout_stage_simulator(world_cup_quater_final_fixtures, stage='Q', tracking_list=quater_final_winners_list)
#Creating Fixtures for Semi Finals
for i in range(0, 4, 2):
world_cup_semi_final_fixtures.append([int((i/2)+1),quater_final_winners_list[i], quater_final_winners_list[i+1]])
#Simulating Semi Finals
print("\n Semi Finals \n")
knockout_stage_simulator(world_cup_semi_final_fixtures, stage='S', tracking_list=[semi_final_winners_list, semi_final_second_list])
#Creating Fixtures for Finals
for i in range(2):
if i % 2 == 0:
world_cup_final_fixtures.append([1 , semi_final_winners_list[0], semi_final_winners_list[1]])
else:
world_cup_final_fixtures.append([0 , semi_final_second_list[0], semi_final_second_list[1]])
#Simulating Quarter Finals
print('\n Finals \n')
knockout_stage_simulator(world_cup_final_fixtures, stage='F')
Создание визуализации
Наконец, я создал визуализацию плей-офф соревнований. Я черпал вдохновение у Серхио Пессоа, чтобы создать этот красивый визуальный ряд.
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 11))
G = nx.balanced_tree(2, 3)
labels = []
list_rev = list(reversed(knockout_games))
for game in list_rev:
label = f"{game[0]} ({game[2]}) \n{game[1]} ({game[3]})"
labels.append(label)
labels_dict = {i:label for i, label in enumerate(labels)}
pos = {0: (226.56, 217.56), 1: (226.56, 289.56), 2: (226.56, 145.56), 3: (328.38, 319.38), 4: (124.73, 319.38), 5: (124.73, 115.73), 6: (328.38, 115.73), 7: (426.12, 300.22), 8: (309.22, 417.12), 9: (143.9, 417.12), 10: (27.0, 300.22), 11: (27.0, 134.9), 12: (143.9, 18.0), 13: (309.22, 18.0), 14: (426.12, 134.9)}
labels_pos = {n: (k[0], k[1]-0.08*k[1]) for n,k in pos.items()}
center = pd.DataFrame(pos).mean(axis=1).mean()
nx.draw(G, pos = pos, with_labels=False, node_color=range(15), edge_color="#d1f4ff", width=10, font_weight='bold',cmap=plt.cm.Blues_r, node_size=5000)
nx.draw_networkx_labels(G, pos = labels_pos, bbox=dict(boxstyle="round,pad=0.3", fc="white", ec="black", lw=.5, alpha=1),
labels=labels_dict)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.show()
Нокаутировать
Заключение
Отвечая на вопрос, который я задал в начале этой статьи, я не уверен в предсказаниях этой модели, поскольку несколько команд, которые вряд ли пройдут групповые этапы, поздно выходят в плей-офф. Однако фаворитом на победу в чемпионате мира является Бразилия, что кажется разумным, а Аргентина выходит в полуфинал, что весьма вероятно. Ожидается, что другая сторона жеребьевки будет неточной: Иран, Катар, Коста-Рика и Уругвай выйдут на этапы конкурса, что будет шоком для большинства. Эти необычные результаты, вероятно, связаны с сильной формой этих более слабых команд, участвующих в турнире. В целом, эту модель можно было бы улучшить, используя больше данных от команд и игроков за более длительный период, потому что короткое окно матчей не позволяло модели предсказывать результаты с большой уверенностью.
Заключительные замечания
Надеюсь, вам понравилось следовать этому уроку. Пожалуйста, найдите мой репозиторий GitHub, если вы хотите попробовать это сами.
Надеюсь, вам понравится чемпионат мира!
Group Stages Group A - Ecuador vs Netherlands : The Game Results in a Draw with a Probability of 0.51 Group A - Ecuador vs Senegal : The Game Results in a Draw with a Probability of 0.71 Group A - Qatar vs Ecuador : The Game Results in a Draw with a Probability of 0.63 Group A - Qatar vs Netherlands : Netherlands Win with a Probability of 0.85 Group A - Qatar vs Senegal : Qatar Win with a Probability of 0.44 Group A - Senegal vs Netherlands : Netherlands Win with a Probability of 0.9 Group A Standings : Netherlands -- 7 Qatar -- 4 Ecuador -- 3 Senegal -- 1 Group B - England vs Iran : Iran Win with a Probability of 0.5 Group B - England vs United States : The Game Results in a Draw with a Probability of 0.36 Group B - England vs Wales : England Win with a Probability of 0.62 Group B - Iran vs United States : The Game Results in a Draw with a Probability of 0.38 Group B - Iran vs Wales : Iran Win with a Probability of 0.74 Group B - United States vs Wales : United States Win with a Probability of 0.56 Group B Standings : Iran -- 7 United States -- 5 England -- 4 Wales -- 0 Group C - Argentina vs Mexico : Argentina Win with a Probability of 0.86 Group C - Argentina vs Poland : Argentina Win with a Probability of 0.76 Group C - Argentina vs Saudi Arabia : Argentina Win with a Probability of 0.83 Group C - Mexico vs Poland : The Game Results in a Draw with a Probability of 0.39 Group C - Saudi Arabia vs Mexico : The Game Results in a Draw with a Probability of 0.56 Group C - Saudi Arabia vs Poland : Poland Win with a Probability of 0.44 Group C Standings : Argentina -- 9 Poland -- 4 Mexico -- 2 Saudi Arabia -- 1 Group D - Australia vs Denmark : Denmark Win with a Probability of 0.65 Group D - Australia vs Tunisia : Australia Win with a Probability of 0.48 Group D - Denmark vs Tunisia : Denmark Win with a Probability of 0.85 Group D - France vs Australia : France Win with a Probability of 0.51 Group D - France vs Denmark : Denmark Win with a Probability of 0.76 Group D - France vs Tunisia : France Win with a Probability of 0.69 Group D Standings : Denmark -- 9 France -- 6 Australia -- 3 Tunisia -- 0 Group E - Costa Rica vs Germany : The Game Results in a Draw with a Probability of 0.46 Group E - Costa Rica vs Japan : Costa Rica Win with a Probability of 0.47 Group E - Germany vs Japan : The Game Results in a Draw with a Probability of 0.58 Group E - Spain vs Costa Rica : Spain Win with a Probability of 0.43 Group E - Spain vs Germany : The Game Results in a Draw with a Probability of 0.67 Group E - Spain vs Japan : Spain Win with a Probability of 0.6 Group E Standings : Spain -- 7 Costa Rica -- 4 Germany -- 3 Japan -- 1 Group F - Belgium vs Canada : Belgium Win with a Probability of 0.45 Group F - Belgium vs Croatia : Croatia Win with a Probability of 0.62 Group F - Belgium vs Morocco : Belgium Win with a Probability of 0.54 Group F - Canada vs Croatia : Croatia Win with a Probability of 0.68 Group F - Canada vs Morocco : Canada Win with a Probability of 0.58 Group F - Morocco vs Croatia : Croatia Win with a Probability of 0.66 Group F Standings : Croatia -- 9 Belgium -- 6 Canada -- 3 Morocco -- 0 Group G - Brazil vs Cameroon : Brazil Win with a Probability of 0.96 Group G - Brazil vs Serbia : Brazil Win with a Probability of 0.85 Group G - Brazil vs Switzerland : Brazil Win with a Probability of 0.85 Group G - Serbia vs Cameroon : Serbia Win with a Probability of 0.88 Group G - Serbia vs Switzerland : Serbia Win with a Probability of 0.71 Group G - Switzerland vs Cameroon : Switzerland Win with a Probability of 0.45 Group G Standings : Brazil -- 9 Serbia -- 6 Switzerland -- 3 Cameroon -- 0 Group H - Ghana vs South Korea : South Korea Win with a Probability of 0.88 Group H - Ghana vs Uruguay : Uruguay Win with a Probability of 0.91 Group H - Portugal vs Ghana : Portugal Win with a Probability of 0.86 Group H - Portugal vs South Korea : Portugal Win with a Probability of 0.59 Group H - Portugal vs Uruguay : Uruguay Win with a Probability of 0.61 Group H - Uruguay vs South Korea : Uruguay Win with a Probability of 0.76 Group H Standings : Uruguay -- 9 Portugal -- 6 South Korea -- 3 Ghana -- 0 Round of 16 Game 1 - Netherlands vs United States : Netherlands Win with a Probability of 0.8 Game 2 - Argentina vs France : Argentina Win with a Probability of 0.72 Game 3 - Spain vs Belgium : Spain Win with a Probability of 0.63 Game 4 - Brazil vs Portugal : Brazil Win with a Probability of 0.74 Game 5 - Iran vs Qatar : Iran Win with a Probability of 0.38 Game 6 - Denmark vs Poland : Denmark Win with a Probability of 0.78 Game 7 - Croatia vs Costa Rica : Costa Rica Win with a Probability of 0.35 Game 8 - Uruguay vs Serbia : Uruguay Win with a Probability of 0.68 Quarter Finals Game 1 - Netherlands vs Argentina : Argentina Win with a Probability of 0.39 Game 2 - Spain vs Brazil : Brazil Win with a Probability of 0.54 Game 3 - Iran vs Denmark : Denmark Win with a Probability of 0.56 Game 4 - Costa Rica vs Uruguay : Uruguay Win with a Probability of 0.53 Semi Finals Game 1 - Argentina vs Brazil : Brazil Win with a Probability of 0.55 Game 2 - Denmark vs Uruguay : Uruguay Win with a Probability of 0.64 Finals World Cup Third Place - Argentina vs Denmark : Argentina Win the World Cup Third Place! with a Probability of 0.69 World Cup Final - Brazil vs Uruguay : Brazil Win the World Cup Final! with a Probability of 0.7